Crawl Policies#
Policy matching#
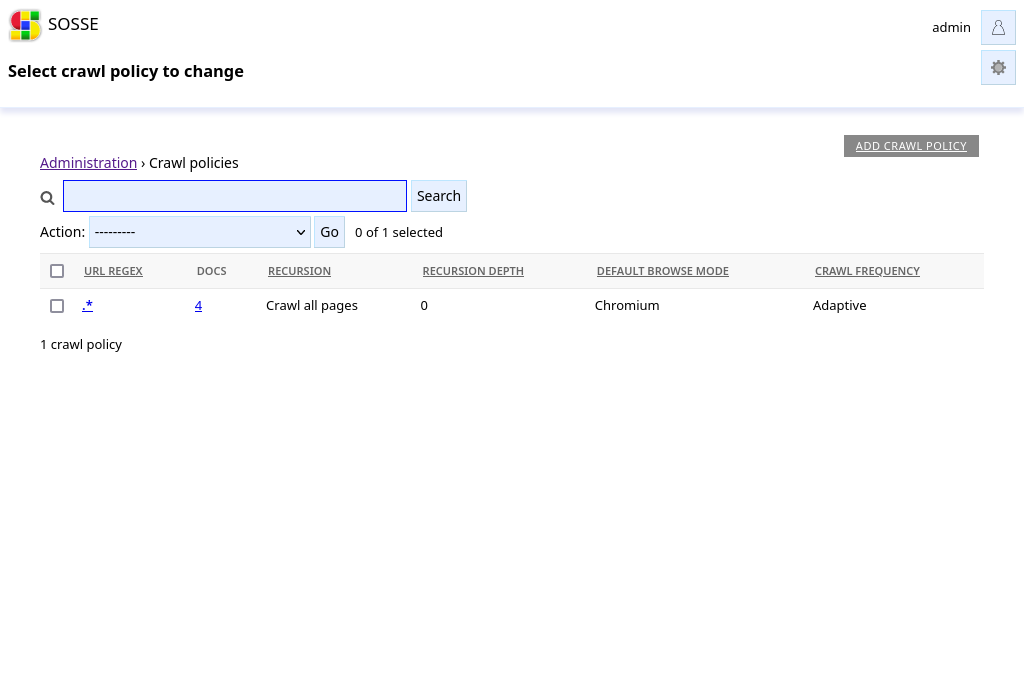
Crawl policies define which pages are indexed and how they are indexed. The policy list can be reached by clicking ⚡ Crawl policies from the Administration interface.
When the crawler indexes a page or evaluates a link to queue it, it will find the best matching policy to know how to handle the link.
The policy with the longest URL regex matching is selected. On last resort, the default policy .* is selected.
You can see which policy would match by typing an URL in the search bar of the ⚡ Crawl policies, or in the 🌐 Crawl a new URL page (see Adding URLs to the crawl queue).
Indexing decision#
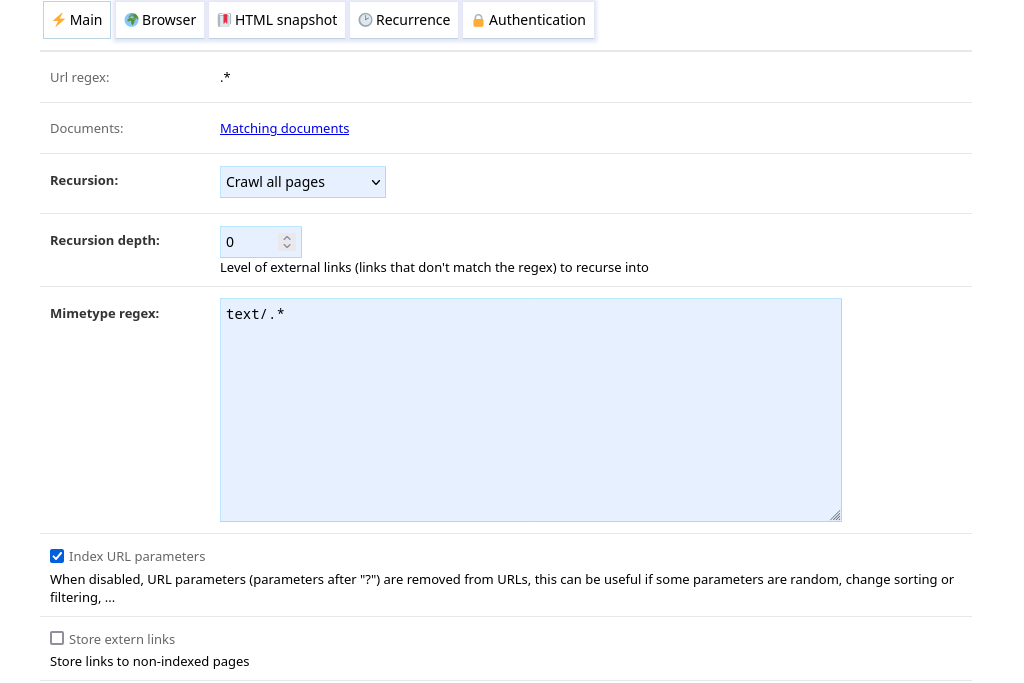
URL regexp#
The regexp matched against URL to crawl. The default .* policy’s regexp cannot be modified.
Documents#
Shows the URLs in the database that match the regexp.
Recursion, recursion depth#
Recursion and Recursion depth parameters define which links to recurse into.
Recursion can be one of:
Crawl all pages: URLs matching the policy will be crawledDepending on depth: URLs matching the policy are crawled depending on the recursion level (see Recursive crawling)Never crawl: URLs matching the policy are not crawled unless they are queued manually (in this case, no recursion occurs)
Recursion depth is only relevant when the Recursion is Crawl all pages and defines the recursion depth for links outside the policy. See Recursive crawling for more explanations.
Mimetype regex#
The mimetype of pages must match the regexp to be crawled.
Index URL parameters#
When enabled, URLs are stored with URLs parameters. Otherwise, URLs parameters are removed before indexing. This can be useful if some parameters are random, change sorting or filtering, …
Store extern links#
When enabled, links to non-indexed pages are stored.
Browser#
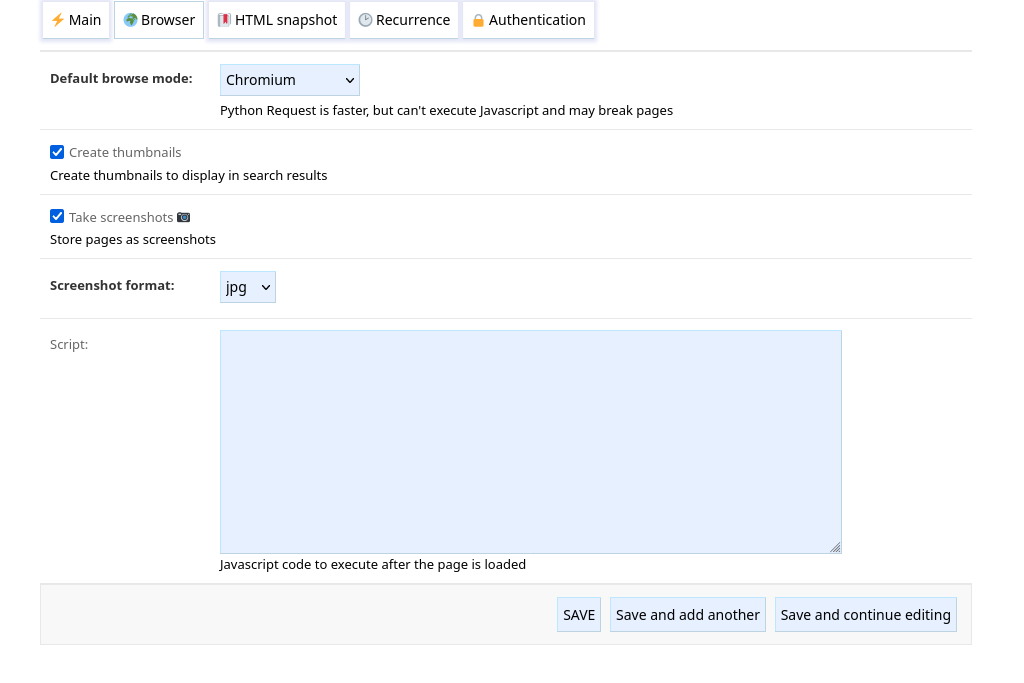
Default browse mode#
Can be one of:
Detect: the first time a domain is accessed, it is crawled with a browser and Python Requests. If the text content varies, it is assumed that the website is dynamic and the browser will be used for subsequent crawling of pages in this domain. If the text content is the same, Python Request will be used since it is faster. By default, the browser used is Chromium, this can be changed with the default_browser option.Chromium: Chromium is used.Firefox: Firefox is used.Python Requests: Python Requests is used.
Create thumbnails#
Make thumbnails of pages. These thumbnails are displayed in search results.
Note
This option requires the Default browse mode to be Chromium or Firefox in order to work.
Take screenshots#
Enables taking screenshots of pages for offline use. When the option Create thumbnails is disabled, the screenshot is displayed in search results instead.
Note
This option requires the Default browse mode to be Chromium or Firefox in order to work.
Screenshot format#
Format of the image JPG or PNG.
Note
This option requires the Default browse mode to be Chromium or Firefox in order to work.
Script#
Javascript code to be executed in the context of the web pages when they have finished loading. This can be used to handle authentication, validate forms, remove headers, …
For example, the following script could be used to click on a GDPR compliance I agree button:
const BUTTON_TEXT = "I agree";
const XPATH_PATTERN = `//*[contains(., "${BUTTON_TEXT}")]`;
const button = document.evaluate(XPATH_PATTERN, document, null, XPathResult.FIRST_ORDERED_NODE_TYPE, null);
if (button && button.singleNodeValue) {
button.singleNodeValue.click();
}
In case the script triggers an error, further processing of the page is aborted and the error message is stored in the document error field. It can be useful to use a tool such as Tampermonkey to debug these kind of script.
Note
This option requires the Default browse mode to be Chromium or Firefox in order to work.
HTML snapshot#
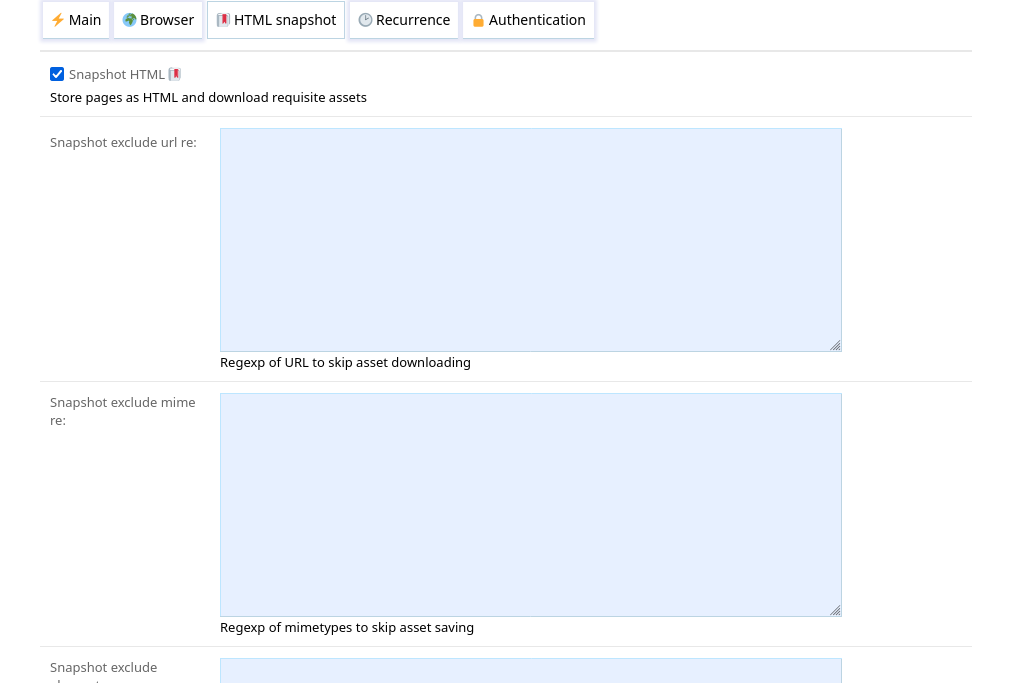
Snapshot html#
This option enables capturing snapshots of crawled HTML pages and there related images, CSS, etc. it relies on for offline use.
A browser can be used to take the snapshot after dynamic content is loaded.
Snapshot exclude url re#
This field defines a regular expression of URL of related assets to skip downloading. For example, setting a regexp of png$ would make the crawler
skip the download of URL ending with png.
Snapshot exclude mime re#
This field defines a regular expression of mimetypes of related assets to skip saving, however files are still downloaded to determine there mimetype.
For example, setting a regexp of image/.* would make the crawler skip saving images.
Snapshot exclude element re#
This field defines a regular expression of HTML element of related assets to skip downloading. For example, setting a regexp of audio|video would make the crawler
skip the download of medias.
Recurrence#
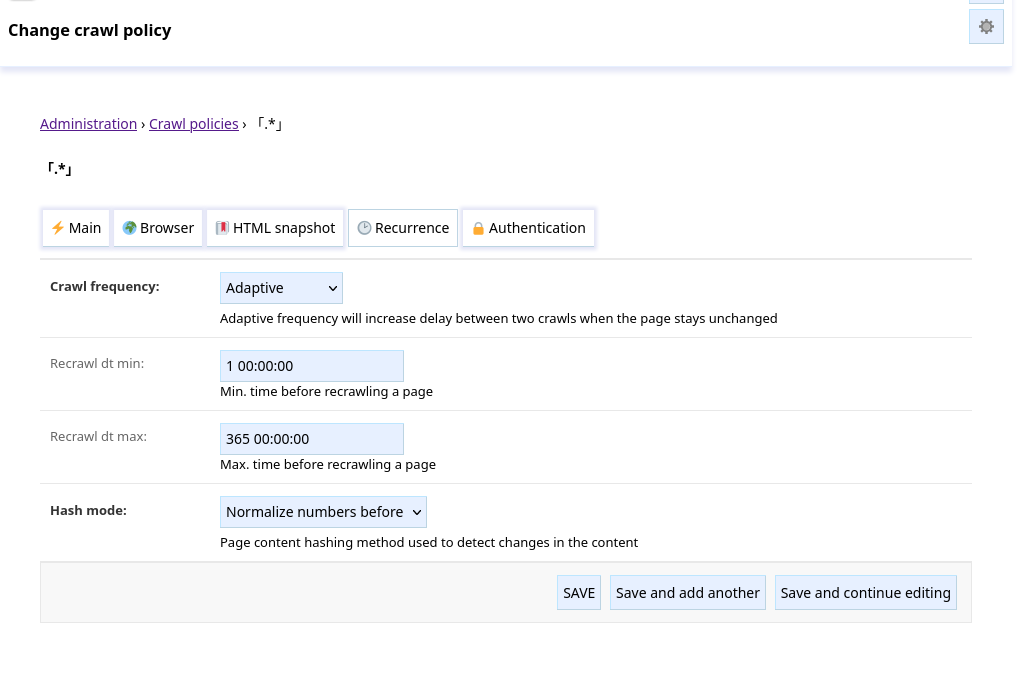
Crawl frequency, Recrawl dt#
How often pages should be reindexed:
Once: pages are not recrawled.Constant: pages are recrawled everyRecrawl dt min.Adaptive: pages recrawled more often when they change. The interval between recrawls starts atRecrawl dt min. Then, when the page is recrawled the interval is multiplied by 2 if the content is unchanged, divided by 2 otherwise. The interval stays enclosed betweenRecrawl dt minandRecrawl dt max.
Hash mode#
Define how changes between recrawl are detected:
Hash raw content: raw text content is compared.Normalize numbers before: numbers are replaced by 0s before comparing, it can be useful to ignore counters, clock changes, …
Authentication#
See Authentication handling for general guidelines on authentication.
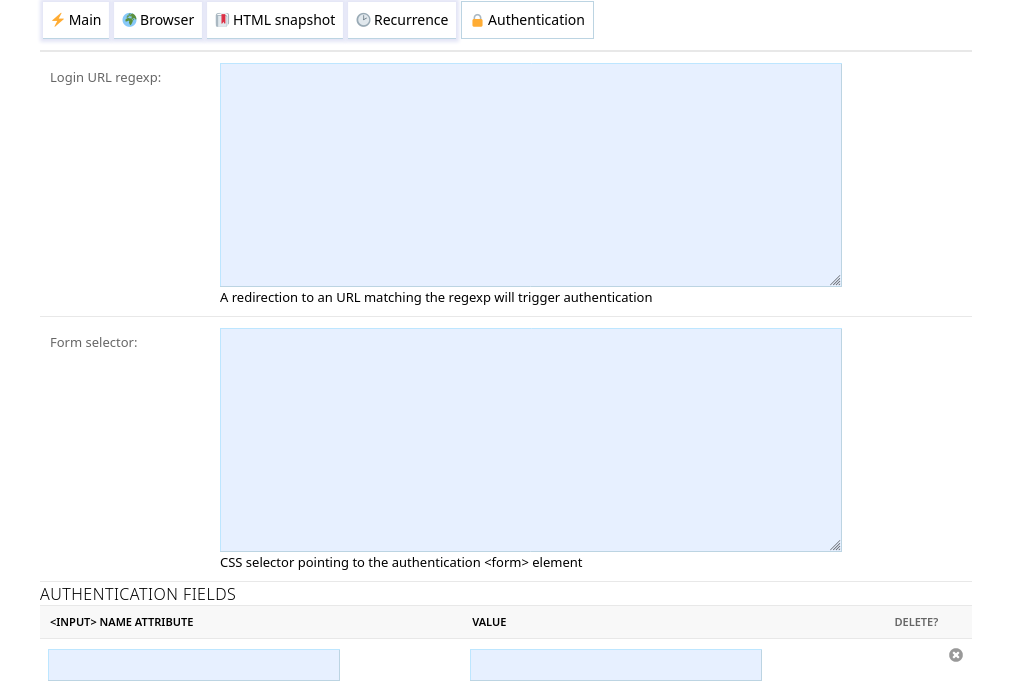
Login URL#
If crawling a page matching the policy gets redirected to the Login URL, the crawler will attempt to authenticate using the parameters definedbelow.
Form selector#
CSS selector pointing to the authentication <form> element.
Authentication fields#
This defines the <input> fields to fill in the form. The fields are matched by their name attribute and filled with the value.
(hidden fields, like CSRF preventing field, are automatically populated by the crawler)